Leak detection carts, known for their efficiency and precision, are widely used for leak detection in various pipelines. This article will delve into the working principles and technical processes of leak detection carts, helping you better understand the technological advantages and operational steps behind them.
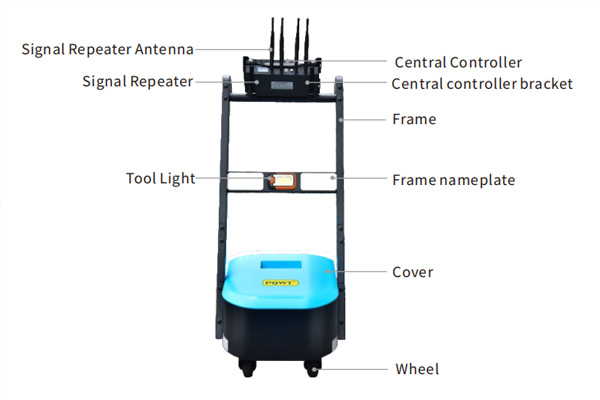

I. Working Principle of Leak Detection Carts
Leak detection carts perform non-destructive testing of underground pipelines through sensors. These sensors typically detect sound waves or other abnormal signals around the pipeline, identifying potential leak points. Once the sensors capture these signals, the data is processed and analyzed by the cart’s onboard computing system, ultimately pinpointing the exact location of the leak.
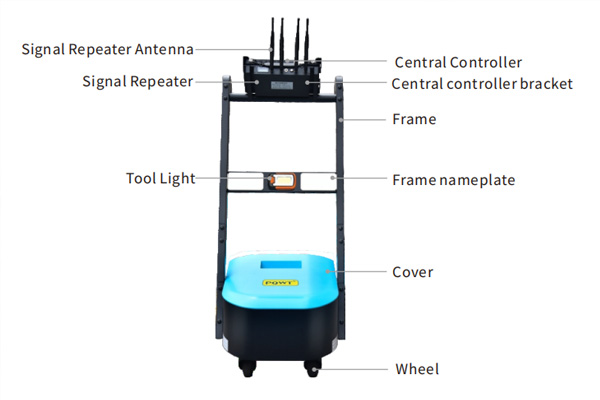
II. Main Technical Components of Leak Detection Carts
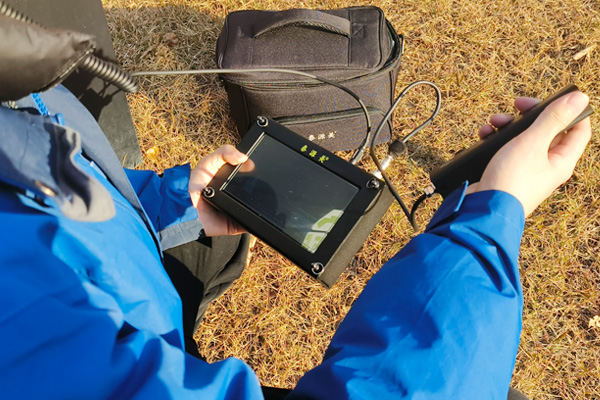
Puqi's leak detection cart uses advanced B-P algorithm technology and is equipped with wireless monitoring sensors. These sensors can simultaneously monitor and record noise signals from pipeline leaks within the probe’s range. The signals are wirelessly transmitted via a signal repeater to a central controller for efficient and rapid analysis. The monitoring results are displayed in real-time on the central controller’s main screen, allowing for automatic identification and differentiation of suspected leak points. The system also allows for real-time audio recording, with collected data being exportable for generating leak reports, thus making inspection and management more convenient.
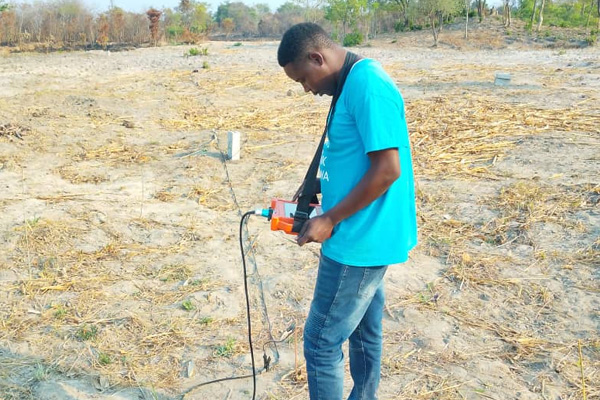
The Puqi leak detection cart uses the acoustic vibration method, which is one of the most widely used leak detection techniques. The device is moved along the surface above the pipeline while detecting leak noise signals. These signals are processed and then fed back into the headphones, where the highest leak signal value is displayed in both sound and frequency spectrum, helping to quickly and efficiently pinpoint the leak's location. This method is relatively simple to operate and is highly efficient, but it requires the operator to have significant practical experience and the ability to analyze and distinguish sound components. Additionally, the site conditions must meet the equipment's requirements.
The Puqi leak detection cart also features a tracer gas detection method. A special mixed gas is injected into the pipeline, and the gas diffuses through the leak, gradually evaporating to the surface. The device is then used to detect the gas concentration along the pipeline’s surface. When the instrument detects the special gas components, it displays the signal and values on the main screen. If the concentration reaches a certain level, an alarm sound will be triggered, indicating the leak’s range. This method is generally used for small leaks, noisy environments, or unpressurized pipelines and requires additional equipment. Detection costs are relatively high, and while it can identify the leak range, it does not pinpoint the exact leak point.
This equipment integrates all three detection functions, allowing for combined use or the use of any single function, greatly improving work efficiency and accuracy. It solves leak detection problems caused by various situations and conditions.
III. Workflow of Leak Detection Carts
1. Equipment Preparation
Before using the leak detection cart, the equipment must be checked to ensure that the sensors, data processing system, and cart mobility system are all functioning properly. The operator should select the appropriate detection mode based on the type of pipeline.
2. Sensor Placement Methods on Site
Based on the optimal layout algorithm for model surface vertex distance differences and axial center distance differences, and according to the principles of the SUMT internal point algorithm, the sensor placement methods are primarily divided into three types: Vertical Placement, Matrix Placement, and Circular Placement.
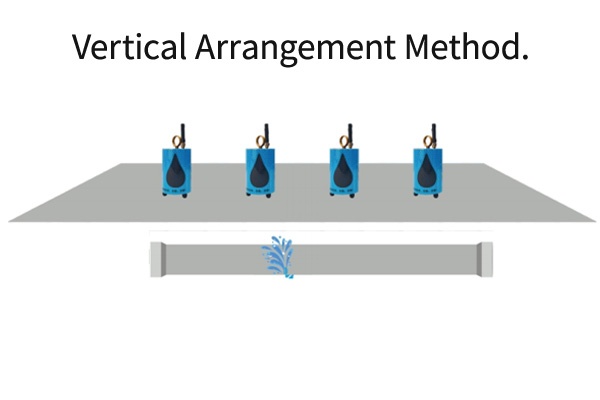
Vertical Placement: Suitable for known pipeline locations, where sensors are placed vertically above the pipeline on the ground. (Illustration provided below)
Matrix Placement: Suitable for suspected leak areas, where sensors are arranged in a grid pattern within the unit area. (Illustration provided below)

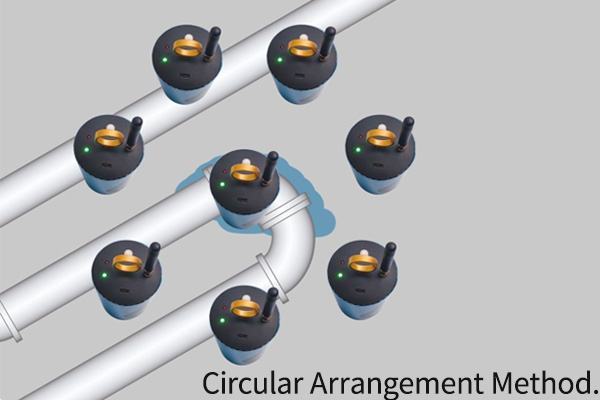
Circular Placement: Suitable for areas around suspected leak points, where sensors are arranged in a circular pattern. (Illustration provided below)
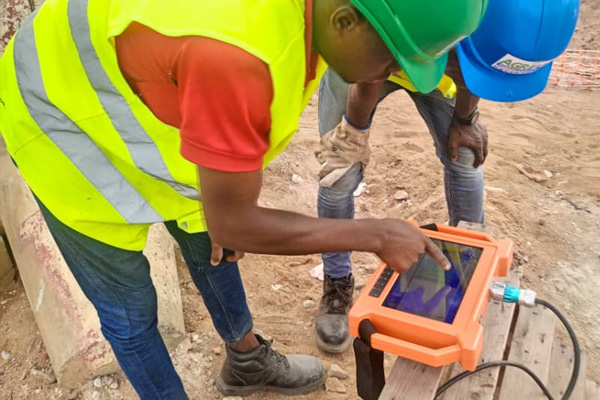
3. Data Analysis and Report Generation
Once the scan is completed, the leak detection cart automatically analyzes the collected data and generates a leak location report. The report details the coordinates and depth of the leak, assisting maintenance personnel with accurate repairs.
Conclusion
The leak detection cart is not just a simple detection tool but a highly integrated system that provides strong support for pipeline maintenance. By understanding its working principles and technical components, you can better appreciate the important role the leak detection cart plays in modern pipeline maintenance.








